Dosing pumps play a crucial role in various industries, facilitating precise control over the dosing of chemicals and fluids in numerous processes. Understanding the fundamentals of dosing pump operation is essential for ensuring efficiency, accuracy, and safety in industrial applications.
What is a dosing pump?
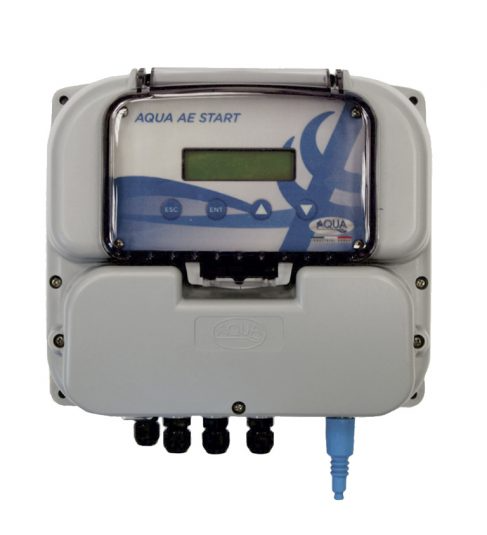
At its core, a dosing pump is a device designed to accurately inject a precise volume of liquid or chemical additive into a system. Unlike traditional pumps that focus on moving fluids in bulk, dosing pumps are engineered for precision and control, making them indispensable in sectors such as water treatment, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing.
Components of a dosing pump:
A typical dosing pump comprises several key components, including a pump head, motor, drive mechanism, suction and discharge lines, and control interface. The pump head houses the mechanism responsible for metering and injecting the desired substance, while the motor and drive mechanism provide the power needed for operation.
Principles of operation:
Dosing pumps operate based on positive displacement principles, ensuring a consistent and accurate flow rate regardless of changes in pressure or viscosity. This is achieved through mechanisms such as diaphragms, pistons, or peristaltic action, which displace a precise volume of fluid with each stroke or rotation.
Types of dosing pumps:
There are various types of dosing pumps available, each suited to specific applications and operating conditions. Diaphragm pumps are commonly used for low-pressure applications and offer excellent chemical resistance, while piston pumps are preferred for high-pressure and high-precision dosing tasks. Peristaltic pumps, on the other hand, are ideal for applications requiring gentle pumping action and minimal maintenance.
Factors influencing dosing pumps performance:
Several factors can impact the performance of a dosing pump, including viscosity of the fluid being pumped, back pressure in the system, temperature fluctuations, and the condition of pump components. Proper calibration, maintenance, and monitoring are essential for ensuring consistent and reliable operation.
Applications of dosing pumps:
Dosing pumps find widespread use across diverse industries, serving purposes such as chemical dosing for water treatment, nutrient delivery in agriculture, precise medication dispensing in healthcare, and additive injection in manufacturing processes. Their versatility and precision make them indispensable tools for achieving desired outcomes in numerous applications.